New targets
- Preview version of aiT for 3rd GEN AURIX 499 (AA-step).
- StackAnalyzer and TimingProfiler for TriCore now support generic TCv1.8 (3rd GEN AURIX TC4x).
AbsInt License Manager (ALM)
- Improved logging into the License Manager when no tokens of the requested type are available.
- Value analysis in interactive mode now only requires one token.
- If you are upgrading your client from a release older than 23.10, make sure to upgrade your License Manager as well. This is necessary due to the new TLS-encrypted connection between the client and the License Manager that was first introduced in release 23.10.

General improvements
- Faster analyses and reduced memory consumption for projects with many configurations.
- Improved support archive creation.
Improved ORTI support
- Improved project import with better handling of vendor-specific extensions.
- Improved heuristics to determine task and ISR entry points.
Wayland support
Added support for client-side decorations.
GUI
- New theme for all icons.
- The option “strip compilation path” is now disabled by default.
- Configurations now allow overwriting more decoding settings such as instruction set, CPU variant etc.
- New go-to-anywhere HUD for quick navigation in the current project, accessible via Ctrl + P.
Visualization and results
- The Analyses overview can now visualize the dependencies between all the individual analysis items.
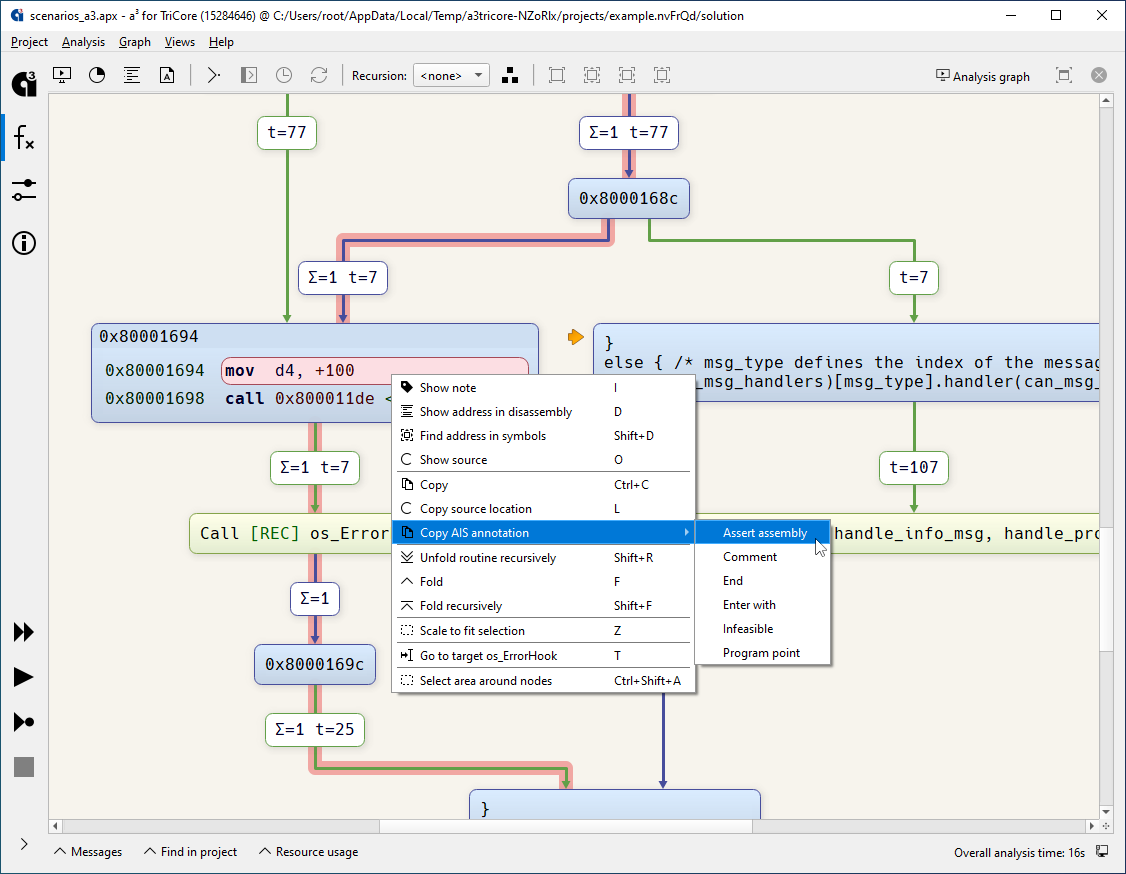
- In the Graph view, the context-menu action “Copy AIS annotation”
now allows to create “
assert assembly” annotations for each instruction. - The context menu entry “Show loop statistics” in the Graph view now honors the selection of an active context and jumps directly to this context in the Statistics view.
- The Symbols view can now be searched for enumerator values.
Annotations
- For a program point offset specification that uses a combination
of instruction classes, the decoder now checks whether the combination
is actually feasible. In other words, each program point specification may only feature:
- at most one of
branch,call, orreturn - at most one of
conditionalorunconditional - at most one of
accessorread - at most one of
accessorwrite
- at most one of
- Improved evaluation of
number_of_parametersandindex_of_parameter. - Improved handling of trace functors nested within expressions that are evaluated during the value analysis phase.
Decoding
- Introduced demangling of Rust symbols using the clang Rust symbol demangler.
- zstd-compressed input files are now automatically decompressed.
- Support for zstd-compressed data dictionary XML files.
- Improved reading of sections for IEEE-695 files. The full section content is now read, and only executable sections are now marked as code.
DWARF
- Support for DWARF debug information for Rust.
- The decoder now utilizes the
DW_AT_noreturnflag for routines to identify whether they never return to the callee.
Reporting
In the XML results file, the possible values for expectation and
analysis_status are now success or fail
(rather than true or false).
Value analysis
- The value analysis now avoids dereferencing NULL pointers
and removes the value
NULLfrom the associated base registers. These are identified by means of the DWARF debug information and the types associated with the base register. If such a NULL pointer dereference is detected, this is reported appropriately in the textual report.
This heuristic is only active if “Use only safe patterns” and “Extract debug information” are enabled under Setup → Decoding. - Improved checking for infeasible control flow by combining relational and value set information with knowledge of taken branch conditions.
- Improved detection of infeasibility for register content contradictions.
- Improved handling of stack-relative memory information.
PowerPC
- Improved automatic switch table decoding and TOC detection for 64-bit DiabData binaries.
- Improved user manual:
- Clarified that guarded memory regions are not supported for MPC5777.
- Clarified memory-access alignment restrictions for MPC7448.
- Definite misaligned accesses for MPC7448 now trigger a warning.
TriCore
- Reworked instruction type classifications.
SYSCALL,TRAPV,TRAPSV,TRAPINV,SVLCX, andBISRperform a read access to determine the new value of register FCX and a write access to save the lower or upper context on the CSA stack. The write access is now also modeled in the decoder. The read access is now modeled in the decoder and the value analysis.MTCRandMTDCRperform a write access to the memory mapped Core SFR (CSFR) space. This write access is now also modeled for the value analysis.RETandRFEperform a read access to restore the upper context registers from the CSA stack and a write access to update free context list. These read and write accesses are now also modeled in the decoder.RSLCXperforms a read access to restore the lower context registers from the CSA stack and a write access to update free context list. These read and write accesses are now also modeled in the decoder.STLCXandSTUCXperform a write access to store the lower/upper context registers in memory. This write access is now also modeled in the decoder.FCALL,FCALLA, andFCALLIperform a write access to save the contents of the link register on the user stack. This write access is now also modeled in the decoder.FRETperforms a read access to restore the contents of the link register from the user stack. This read access is now also modeled in the decoder.ST.Tperforms a read and a write access to change a single bit in memory. These read and write accesses are now also modeled in the decoder.
These changes can affect AIS2 annotations that use
-> read(n),-> write(n), or-> access(n)to locate a program point if they span over the aforementioned instructions. - For AURIX, the CSFR
core_idis now modeled directly as a register instead of being memory-mapped. Thus, it can now be used in AIS2 expressions viareg("core_id"). - Improved handling of:
TRAPINV- division by zero
- CSA chain initialization in OS code
- core-local code and data scratch pad memories for generic AURIX
- Improved automatic switch table decoding for GCC.
Other target architectures
- Am486: Bus jitter is now kept concrete to improve analysis precision.
- HCS12(X): Correct memory accesses for fuzzy logic instructions.
- M68k: Improved automatic switch table decoding for Microtec.
- S12Z: Improved automatic switch table decoding for CodeWarrior.
TimeWeaver
- Trace coverage statistics now include flow coverage. This information can be used to identify bad trace coverage by determining how many outgoing edges have been traced per incoming edge of a basic block.
- Improved trace coverage statistics for external routines.
- Improved handling of trace snippet starts, and improved end handling for block-level traces.
- Improved handling of user-annotated end points.
- Improved visualization of trace segments that start or end in external routines.
- General improvements to trace segment visualization.
- Improved support for ARM ULINKpro CSV traces.
Qualification Support Kits
- New packages:
- QSK for StackAnalyzer for PPC (instruction set 64, generic)
- QSK for StackAnalyzer for PPC (instruction set 64, compiler-specific: diab-5.9.7.1)
- New test case
qk_ais2_computed_targetsfor all architectures. It combines and supersedes the test casesqk_ais2_computed_*_targets, and additionally checks for the new AIS2 annotationtargets. - Traval-based measurement test cases have been optimized to no longer perform an unnecessary aiT analysis.
- Compiler-specific test cases that only deal with decoding results have been optimized to only perform value analyses rather than unnecessary timing or stack analyses.
- The AIS2 attribute
core_idis now only checked for the target types that export it. - Added a missing header file for stack measurement test cases.